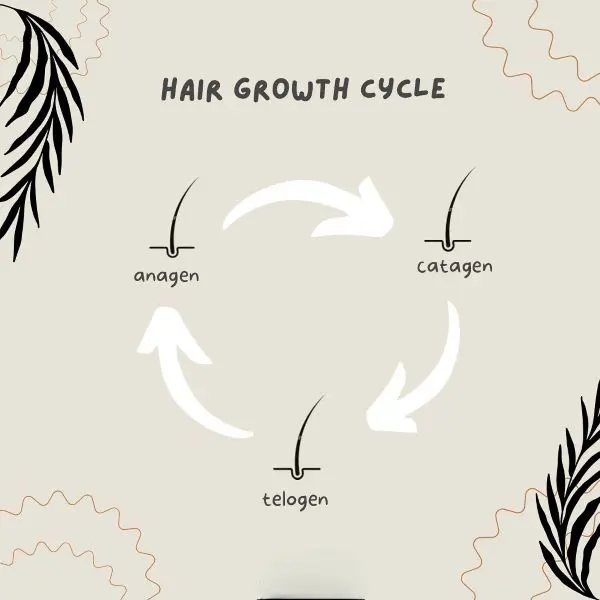
If you desire to know more about a fascinating process going on beneath your hairline, studying the stages of hair growth is a great starting point.
No wonder people don't have identical hair, and every strand behaves uniquely. In addition, each strand may react differently when going into the growth, rest, or fallout phases.
Awareness of these stages would help you understand the whole cycle of hair development and the various factors involved.
Read on and discover a detailed guide to help you understand these stages.
Stage 1: Anagen Phase (Growing Phase)

The anagen phase is the period of active hair growth, where hair extends from the roots. It plays a crucial role in promoting the appearance of hair from the base.
Compared to the other stages of hair growth male, this phase is significantly longer. During this phase, the cells of the hair follicle rapidly divide and produce keratins that form the hair shaft.
Duration Of The Anagen Phase
Anagen length determines how long the hair can grow in individuals in a month. During this phase, hair usually grows around one-half inch (1.25 cm) a month, though genetic factors can affect this rate.
Wondering how long this phase will last for? It's between two to six years. People with a longer anagen phase typically have longer hair.
Sign Of Anagen Phase

A healthy anagen phase is characterized by:
• Consistent Hair Growth: One of the basic requirements of a very healthy anagen phase is regular and steady growth of hairs.
• Strongly Thick Hair: Thick strong hairs during the anagen phase are indicative of normal functioning of follicles.
• Longer Times Between Shedding: A prolonged anagen phase results in fewer hairs entering the resting phase, leading to reduced shedding.
Factors That Affect The Anagen Phase
-
Genetics

Your genetic strain is one of the most crucial factors, which would primarily determine the length and health of an anagen phase.
Genes actually determine the growth cycle, including the duration of anagen follicles stay in.
If your parents had thick, long hair and maintained it for a long period, it’s likely you might share similar traits.
Conversely, if your family tends to have shorter, thinner hair, your anagen phase may be shorter, leading to slower or less dense hair growth.
-
Hormones
Hormonal variation influences hair growth changes quite drastically during periods such as adolescence, gestation, and the cessation of monthly bleeding.
An example of this is that increased estrogen produced by the body during pregnancy extends the anagen stage in hair growth, leaving hair a bit fuller and denser.
Conversely, during menopause, estrogen goes down and testosterone goes up and can lead to hair thinning or hair loss due to a shortening of the anagen phase in some persons.
-
Health And Nutrition

Healthy nutrition has a strong impact on an individual's overall health and growth of hair. A healthy body will normally act toward hair follicles and nutrient deficiencies will adversely affect the anagen phase.
A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, combined with sufficient fluid intake, supports growth cycles in hair and prolongs and improves the anagen phase.
-
Age
As we start growing old, the length of the anagen phase typically shortens. This means hair may spend less time in the growing phase than when one was younger.
With reduced secretion of the growth-promoting hormones and slower cell turnover, hair tends to become thinner, weaker, and shorter in hair cycle.
Stage 2: Catagen Phase (Transition Phase)

Following the anagen phase, the catagen phase serves as a short transition period where hair growth ceases, and shedding begins.
Duration Of Catagen Phase
The catagen phase is generally from 2 to 3 weeks.
Signs Of Catagen Phase
During the catagen phase, you may notice:
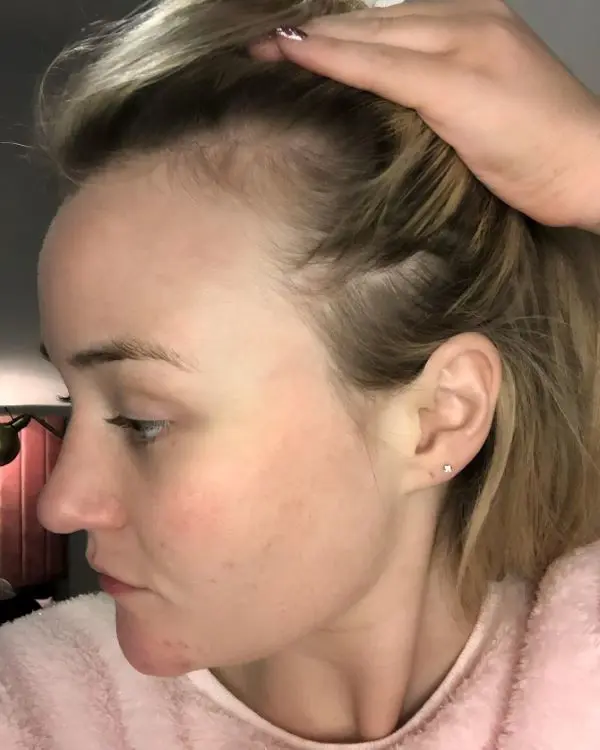

• Reduced Hair Growth: Hair growth halts or reduces drastically, with only 1% of the hairs on the scalp in this stage.
• Minimal Hair Shedding: Unlike the telogen phase, hairs do not shed immediately in this stage. The hair follicles reduce in size by about 70%
• Thinning Of Follicles: The bulb of the hair root diminishes in size and hardens into a club shape, influenced by the nutrient-providing dermal papilla.
Factors That Affect Catagen Phase

-
Health Conditions
Unlike the anagen phase, where health largely influences growth, disruptions during the catagen phase can prematurely halt the natural transition of hair follicles.
Conditions such as alopecia areata or severe nutritional deficiencies can trigger abnormal patterns in the catagen phase.
For instance, iron deficiency anemia and protein malnutrition are known to disturb the cycle’s balance, leading to hair loss issues.
-
Stress
Chronic stress is a significant factor that can disturb the stages of facial hair growth.
Any form of stress that the body encounters during the catagen phase is able to prompt an immediate shift to the telogen phase thus causing hair breakage known as telogen effluvium.
If this condition is left unattended, one will recognize a decline in hair density since more hairs stop in the growth cycle phase.
-
Environmental Factors

Pollutants in the environment including the heavy metals, toxin, and ultraviolet light exposure harm the health of the hair follicle disrupting its growth cycle for hair.
Prolonged use of these compounds results in oxidative stress that affects the follicles and hasty effects may lead to transition to the catagen phase.
-
Seasonal Changes
Seasonal shifts can subtly affect the catagen phase. Research suggests that in some people, hair follicles may be influenced by seasonal cycles, with increased shedding in late summer or fall.
This phenomenon is thought to be related to evolutionary traits where hair growth patterns are adapted to environmental needs, such as temperature regulation.
Stage 3: Telogen Phase (Resting Phase)

The follicle remains inactive in the shortest phase of the hair’s growth cycle, which is referred to as the telogen phase. The hairs do not drop off during this time, staying attached until they naturally shed or are replaced by new growth.
Duration Of The Telogen phase
The precise length of this phase is around two to four months, with hairs that were ten to fifteen percent in telogen at any one time in the scalp.
Signs Of The Telogen Phase

• Hair Shedding: You may notice hairs with a small, white bulb at the root when they shed naturally.
• Stable Length: Hair strands do not grow longer during this phase.
• Thinning: An increased number of hairs in the telogen phase may lead to temporary hair thinning.
Factors That Affect Telogen Phase
-
Pregnancy And Postpartum Period
The normal hormonal changes that occur in pregnancy are really dramatic where hair growth cycles are concerned in the postpartum period.
At childbirth, the body experiences a drastic hormonal drop, especially that of estrogen, which may lead to the phenomenon where an excessive number of hair follicles in the anagen phase will simultaneously enter the telogen phase.
-
Sleep Patterns

Chronic sleep deprivation or poor sleep quality can impact the body’s overall health, including fast hair growth.
Poor quality sleeping or chronic sleeplessness brings about homeostatic imbalances, raises stress levels, and prevents the processes of cell repair and regeneration.
All these functions impact the longer telogen and better quality sleep that helps maintain a proper balanced hair cycle.
-
Excessive Hair Manipulation
Constantly manipulation or traumatizing the hair can trigger the telogen phase prematurely. These actions can damage hair follicles and disrupt the cycle, leading to shedding and delayed regrowth.
Protecting the hair from excessive mechanical stress helps prevent premature entry into the telogen phase and supports follicle health.
-
Dehydration

The lack of water in the body can have unhealthy impacts on the hair follicles depriving them a much needed nutrient and moisture.
The body tends to conserve water to ensure heart functions and organ health as well as moments needed to restore the head’s hair-follicle health, sending it to the telogen stage.
Stage 4: Exogen Phase (Shedding Phase)

The exogen phase refers to the period when hair naturally sheds from the scalp. It is the process of hair fall that occurs at the end of the telogen phase.
This phase typically overlaps with the telogen phase and marks the end of the hair growth cycle for a particular strand.
Duration Of The Exogen Phase
The exogen phase typically lasts several weeks, and the shedding of hair can occur gradually over time.
In this phase hairs shed between 50 to 100 hairs on a daily basis and this is perfectly normal for individuals with healthy hair.
Sign Of The Exogen Phase
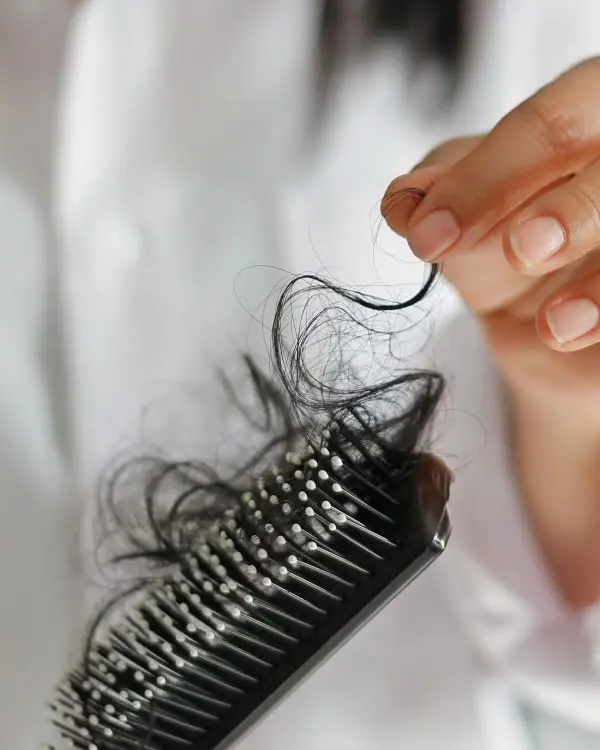

• Hair Loss: The initial sign is easily recognized as the loss of hair strands. Whatever you use for washing your hair, you may observe that you get more hair on it than usual before.
• Thinning Hair: As hair sheds, the overall volume may appear reduced temporarily until the new growth cycle begins.
• Hair Comes Out Easily: During this phase, hair pulling is easy-for example, there's little effort required when combing or washing hair.
Factors That Affect Exogen Phase
-
Chemical Damage And Styling

Frequent use of harsh chemical treatments such as dyes, perms, or relaxers can weaken hair and promote excessive shedding.
Likewise, heat styling and physical damage to the hair can harm the follicles, triggering early shedding during the exogen phase.
Over time, these factors naturally disrupt the hair cycle, thereby increasing the shedding state of hair.
-
Poor Scalp Health
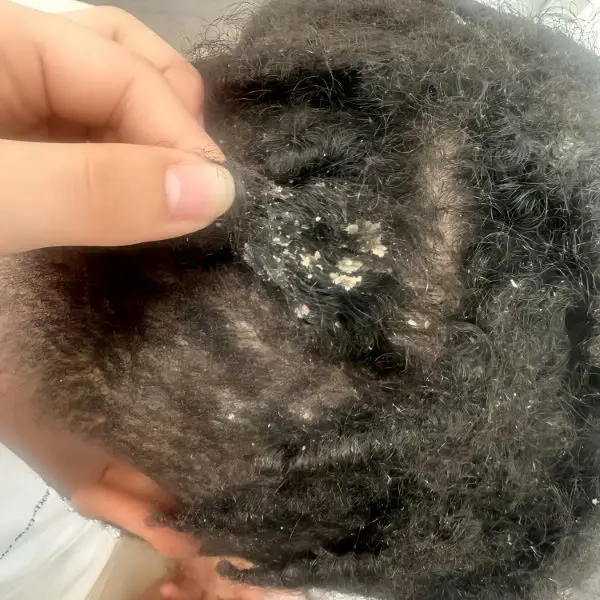
Some kinds of unhealthy conditions of the scalp play a hindrance to the process of shedding.
Seborrheic dermatitis or psoriasis as well as any fungal infection would affect the hair follicles and lead to premature shedding.
An irritated or infected scalp can hamper the hair growth causing more hair to enter into the exogen phase.
It is utmost important to keep the scalp clean, healthy and infection- free to lessen excessive shedding in the exogen phase.
-
Excessive Weight Loss Or Rapid Weight Changes
Rapid or severe weight loss, whether caused by illness or dieting, can interfere with the hair growth stages, pushing the body into survival mode and resulting in premature shedding during the exogen phase.
This is particularly common after significant caloric restriction or after bariatric surgery.
-
Hair Care Products

The type of hair care products used can also impact the exogen phase and the overall duration of hair growth.
Products containing sulfates, alcohol, shampoos, and conditioner are notorious in damaging the hair follicles leading to breakages.
Tips For Supporting Healthy Hair Growth
To healthy hair and growth:
• Balanced Diet: Protein, biotin and omega-3 fatty acids should also contain vitamin A, C, and E.
• Gentle Hair Care: Avoid excessive heat, rough chemistry, and tight hairstyles, which can harm the follicles. Instead, try using homemade conditioner for harmless enhancement.
• Managing Stress: Modern approaches to relaxation often involve yoga and meditation.
• Hydration: Drinking enough water ensures the scalp stays healthy and nourished.
• Consult a Professional: Profound hair loss with hair scalp questions should be referred to a dermatologist or trichologist.