Eyes are associated with warmth and sincerity and are often seen as a reflection of a person's personality. Eyes color ranges from dominant brown to rare gray where all the types are equally unique.
The diversity in eye color is due to the amount and type of pigments in the iris, the colored part of the eye. The genetics of eye color is complex, with multiple genes influencing the final outcome.
Here, we take a look at these beautiful differences.
Common Eye Colors
Eye colors are a fascinating spectrum that adds a splash of diversity to human appearances. The most common eye colors include brown, blue, green and hazel which make the prime categories.
1. Brown Eyes
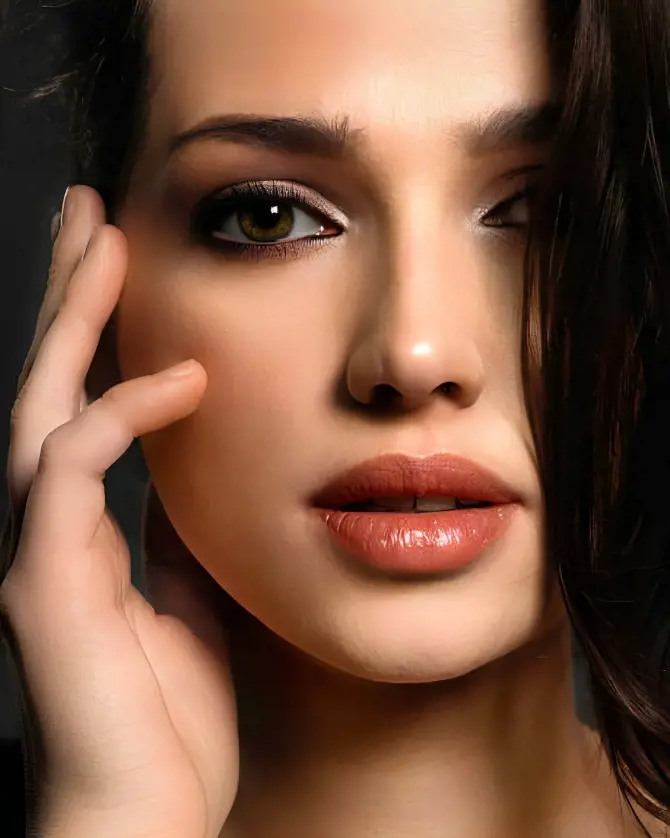

This is the most frequent and widely dispersed eye color adorning the irises of more than fifty percent of people worldwide which makes it the most common color.
Its prevalence is due to a larger concentration of melanin in the iris that gives the eyes their distinctive brown color.
Brown eyes can range from deep almost black tones to lighter honey-toned varieties which is common among people of African, Asian and Native American descent.
The warmth and richness of this color provide a touch of timeless charm to the glance which makes them a captivating element in the human tapestry.
2. Blue Eyes
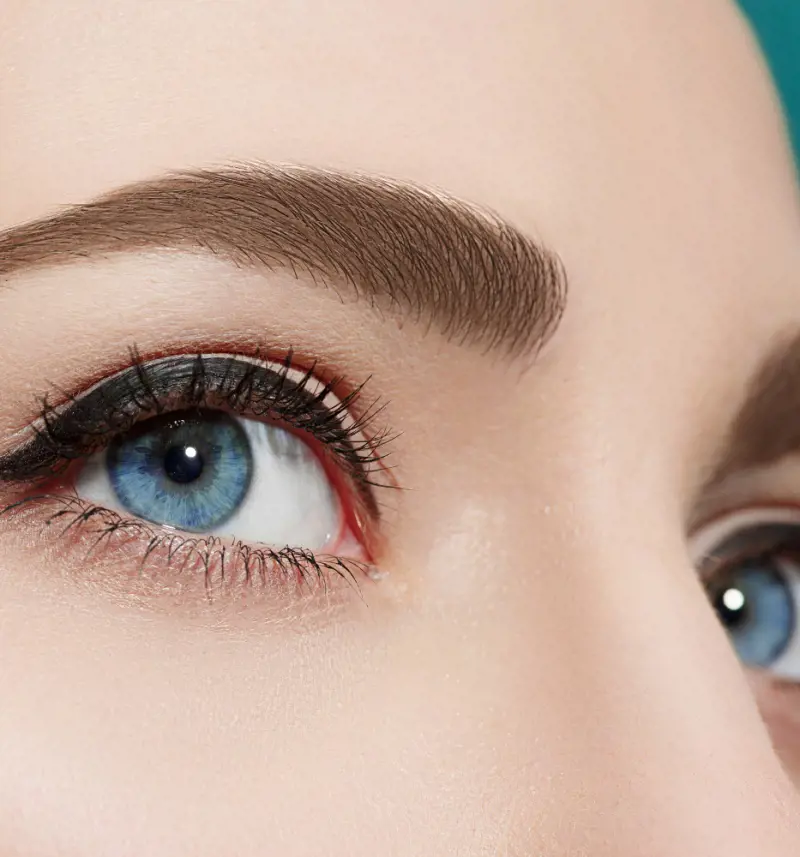

This coloring is a fascinating and unusual ocular characteristic that captivates due to its rarity and appeal.
It is distinguished by a lack of melanin in the iris which allows light to scatter and reflect resulting in a striking azure hue.
Blue eyes are not merely a beauty feature, rather they also have hereditary importance and it is mostly connected with people of European heritage.
This ethereal eye color is a beautiful treat and evidence of the delicate interplay of genetics and geography that produces our distinctive human fabric.
3. Green Eyes
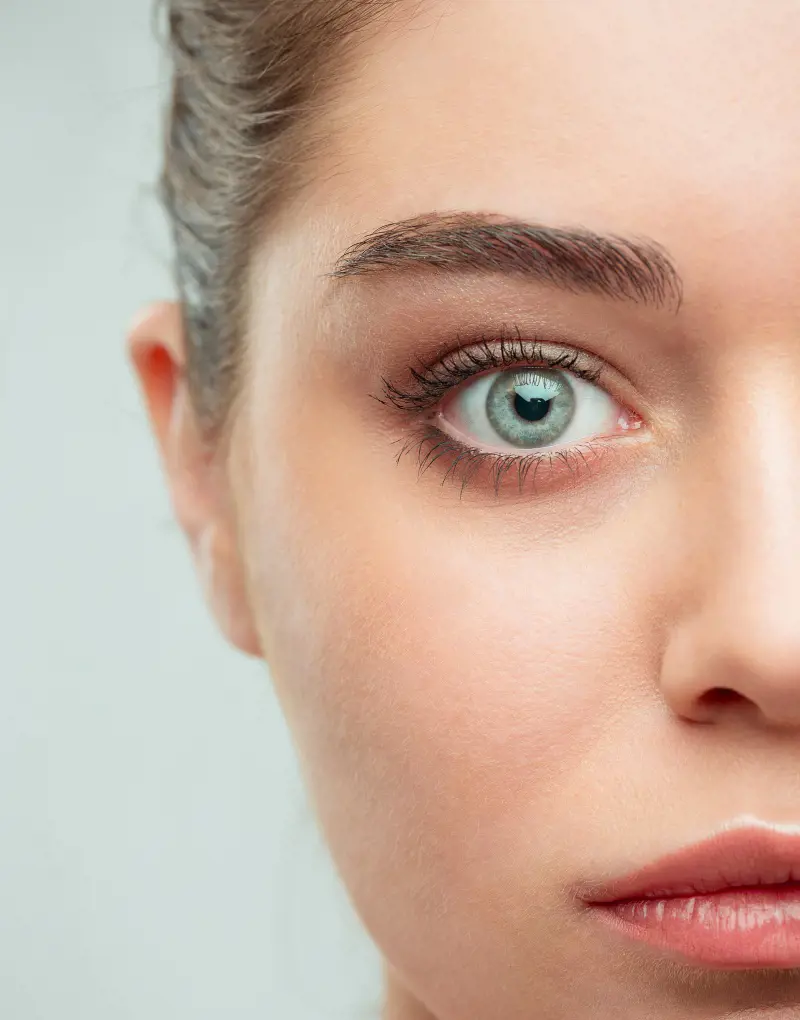

This is a mesmerizing attribute that only a small percentage of the worldwide population possesses.
These types of eyes are distinguished by their distinct blend of blue and yellow pigments which results in a color reminiscent of emerald or jade.
The entrancing green hue is frequently connected with mystery and appeal and is typically seen in people of European heritage.
The highest occurrence is found in Iceland and Scotland where more than twenty percent of the population has this remarkable eye color.
4. Hazel Eyes
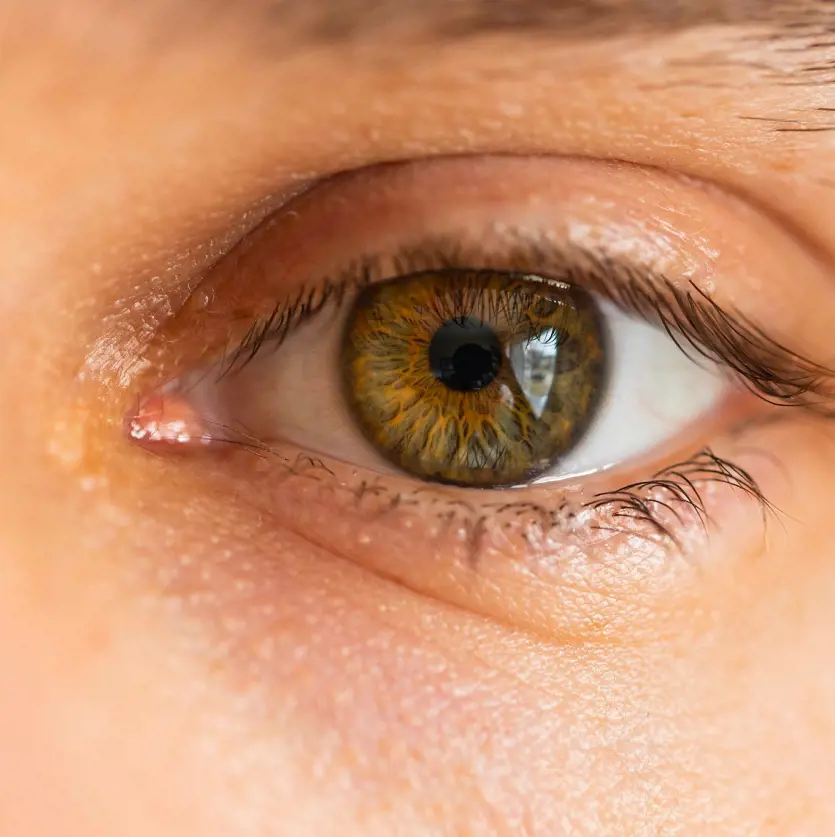
This unique eye color has a dynamic and ever-changing appearance based on lighting and circumstances.
If you are wondering what color are hazel eyes, it has a blend of green, brown and traces of gold.
This distinct eye color is frequently associated with people of European, Middle Eastern and North African ancestry.
This intriguing blend of colors is more common in areas with a mix of genetic backgrounds and bears a capacity to fluctuate between tints.
This effect creates a mysterious and alluring glance that adds an added depth of mystery to the eyes and exemplifies the beauty of genetic variation.
5. Pink or Red Eyes
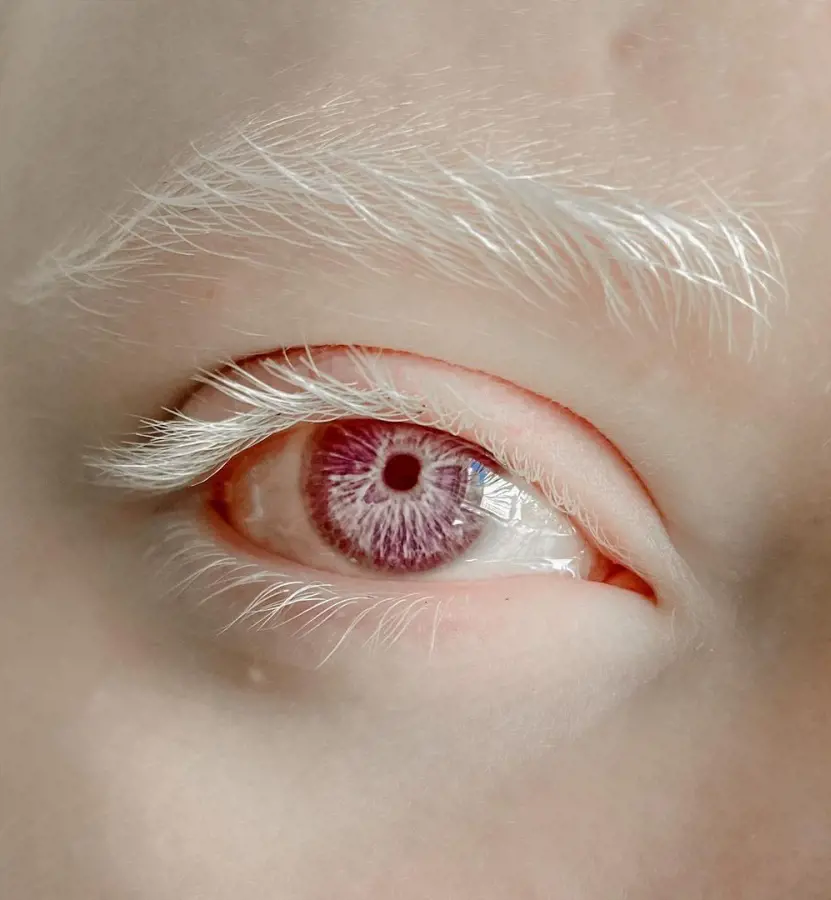
This is an uncommon and intriguing hue that develops as a delicate blend of pale red and mild pink tones.
Also known as albinism, it has a remarkable and otherworldly appearance setting it apart from more frequent colors.
Pink eyes are rare and mysterious and most commonly linked with certain ethnic groups of East Asian nations.
It serves as a reminder that the palette of human uniqueness extends beyond the typical range of eye colors, creating a stunning mosaic across the globe.
Rarest Eye Colors
It is commonplace to see eyes with hues of brown, blue and green but there are individuals who have entirely different colors.
Shades like amber, violet, and heterochromia are like rare masterpieces which makes them stand out in the crowd.
Gray Eye Color

This rare and intriguing eye color is distinguished by its subtle shifting tones that range from a stormy steely gray to a gentler silver tint.
People with this eye color emanate mystery and create enigmatic attractiveness due to the chameleon-like character of their eyes.
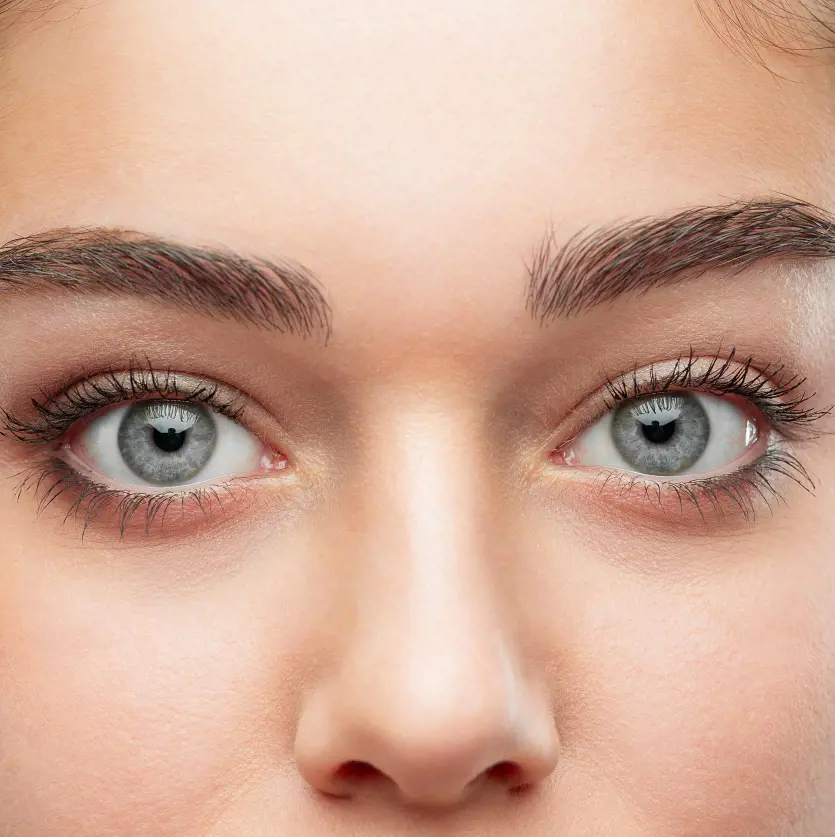

Gray eyes are distinguished by their capacity to reflect and magnify surrounding colors while responding to changing lighting situations and emotions.
Gray eyes are also generally linked with depth and wisdom which adds to their rarity and allure.
Heterochromia (Eyes with Different Colors)
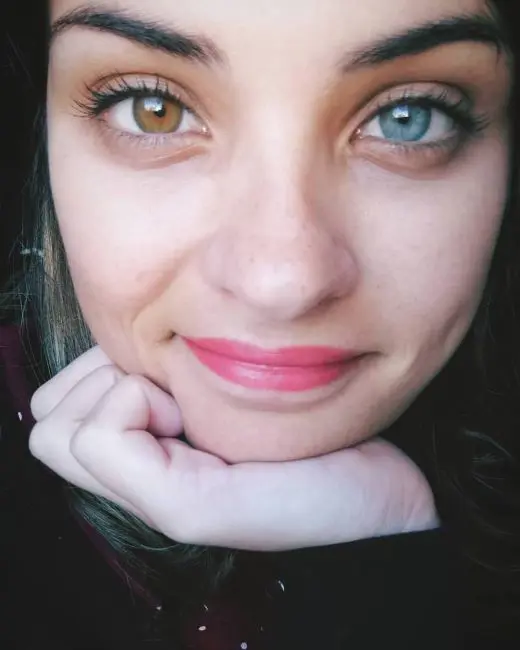

This is a rare phenomenon or uncommon disorder where a person has two different eye colors within the same gaze, giving each eye a distinct hue.
This occurrence is also known as heterochromia caused by the interplay of clashing colors which creates a visual tapestry that reflects the person's individuality.
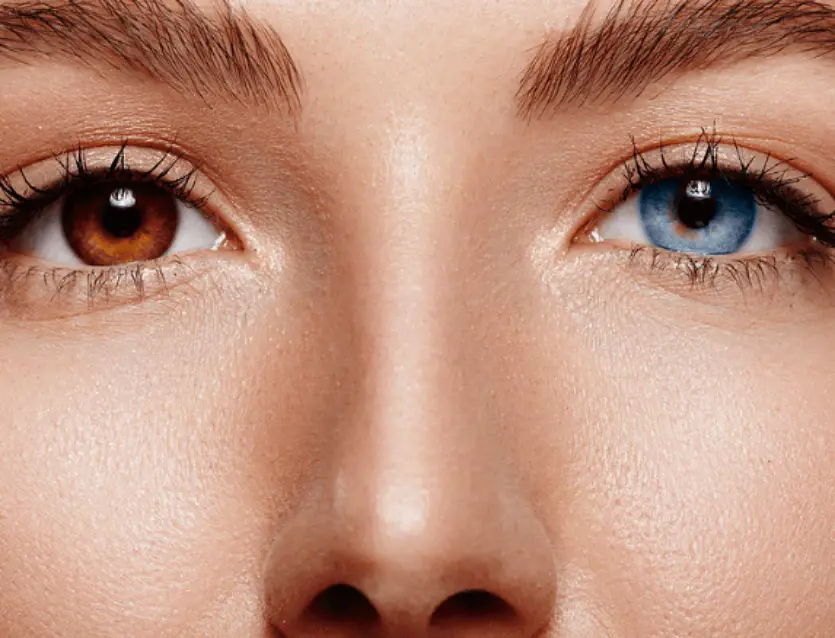

It can be total heterochromia in which each eye is completely different in hue or sectoral heterochromia in which a component of one or both eyes is a distinct shade.
This enthralling attribute is not only a genetic aberration but also a monument to the remarkable diversity contained inside the human genome.
Determining Factor Of Eye Color
The main factor that influences the color of your eyes is the synthesis of melanin or pigments in the iris. More melanin means darker eyes whereas less melanin means lighter eyes. Let's take a look at the factors that determine the eye color.
Genetics

Recent discoveries have discovered that the determination of eye color goes beyond the arena of dominant and recessive genes.
The majority of eye-color genes are involved in the transport, manufacture and storage of melanin.
To put simply, more melanin in the iris results in brown eyes while less melanin results in blue, hazel, green or gray eyes.
Similarly the quantity of melanin present in the front, back and stroma layer between the iris is also important.
Eumelanin causes darker eyes and Pheomelanin is responsible for the appearance of green or amber eyes.
People living in countries farthest from the equator have lighter-colored eyes and skin while darker eyes and skin are more common in warmer climates near the equator.
Age

Age is an important factor to be kept under account when it comes to the color of the eyes.
For instance, if you don't have gray eyes but notice that they are becoming grayer over time, this could be due to a cataract.
Adult eye color might shift and take on a more unusual appearance which is not always a cause for concern. But cataracts can impair your vision and may require surgical removal.
Other times you may experience the clouding of the lens of the eyes and brown freckles can form in your iris over time. This is the result of sun exposure which is harmless, however, some can be malignant.
What Does Your Eye Color Suggest?
A person can experience a change in eye color due to several factors such as heredity, disease or trauma. Some drugs used to treat glaucoma, a disorder that causes high eye pressure, can also result in the eye color shifting over time.
Eye Colors and Risks
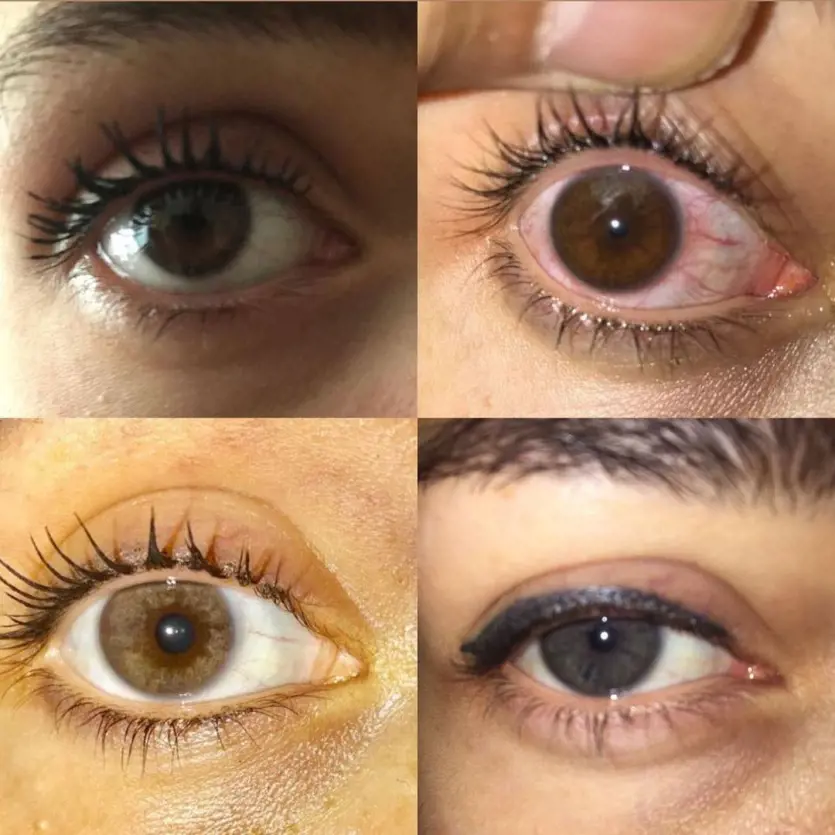
Light-colored eyes may indicate an increased risk of skin cancer compared to darker eyes. Light colors have a higher risk of melanoma of the uvea, the main layer of the eye that includes the iris.
Melanoma of the uvea is a rare malignancy that affects five to six out of every one million persons in the United States each year. Other risk factors for this disease include medical problems such as congenital ocular melanocytosis or ocular melanocytoma which is usually caused by a gene mutation.
Eye Color and Light Sensitivity
People with blue eyes have the greatest possibility of experiencing increased glare, hazy vision and decreased contrast due to intraocular straylight. This is a phenomenon in which light passing through the eye is scattered.
People with blue eyes have decreased melanin pigment in the front layer of their iris which causes light to scatter and absorb some of the longer wavelengths. Usiwoma Abugo, MD, an ophthalmologist says this is how their eyes get their blue color reminiscent of the sky.

Color of the White (Sclera)
Irises may not give you the complete picture of your health but certain changes in the appearance of your eyes could signal some underlying conditions.
Red Whites:
If the white area of your eyes known as the sclera turns red, it indicates anything from conjunctivitis to a subconjunctival hemorrhage. When this part appears red and swollen, it could be a symptom of an autoimmune disease.
Yellow Whites:
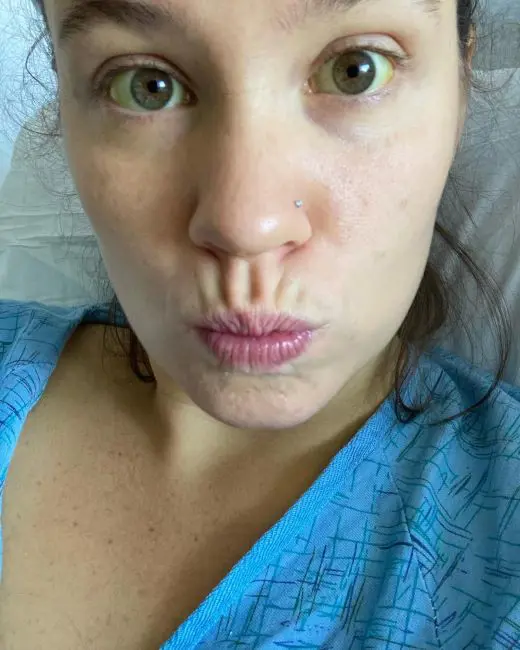
The yellowing of the whites of the eyes is called Jaundice which causes the entire sclera to seem yellowish. It is also possible to develop a yellow spot or lump in the conjunctiva, the clear layer of tissue that covers the sclera.
White Corneal Ring:
Developing a gray or white ring around your cornea is normally not a cause for alarm but a sign of an underlying problem. This means you could have atherosclerotic disease or advanced carotid vascular disease.
This Is How To Take Care Of Your Eyes
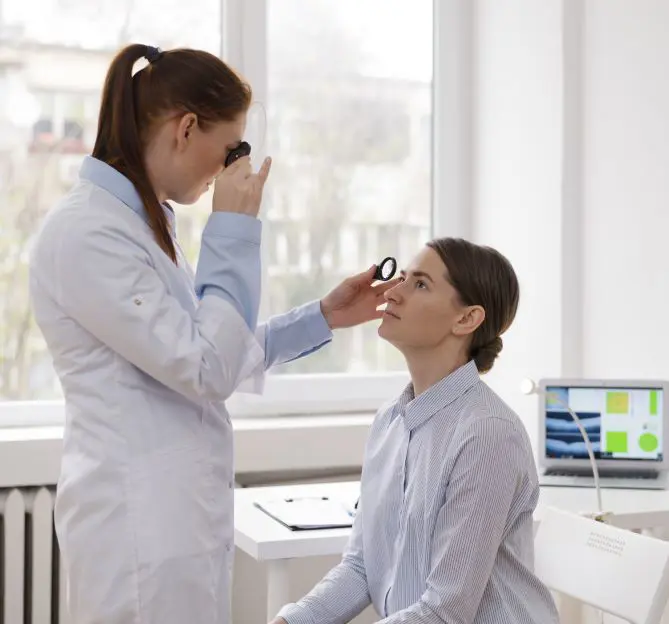

Annual eye exams help you stay on top of any changes in your eyes that may indicate an underlying ailment or deeper issue.
Eye color can be indicative of a pre-existing ailment rather than possible problems.
You can take care of your delicate sense organs by wearing sunglasses with UV protection to shield them from harmful rays and using warm eyeshadow colors.
Use bold and dark mascara to define the lashes and apply sunscreen around the eyes.










